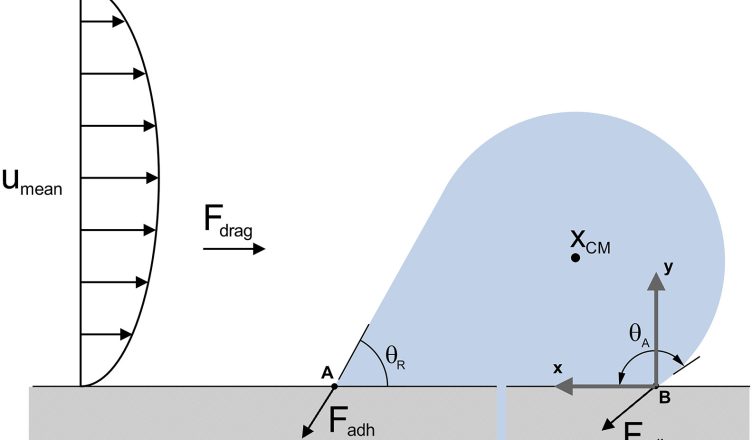
A semi-analytical model for droplet dynamics on the GDL surface of a PEM fuel cell cathode
In this work, a semi-analytical model of a water droplet emerging from a gas diffusion layer pore in a PEFC channel is developed. From the analysis of the drag coefficient it can be concluded that using a spherical drop drag equation versus Reynolds number leads to underpredicted values of the drag coefficient and therefore the drag force. The results for the adhesion force show that the considered equation gives higher results than others obtained from a spring model [1], [2]. The value of the critical drag force corresponding to the droplet detachment is consistent with the experimental data in reference [3]. The detachment condition from reference [3] has been tested comparing the experimental data from reference [4]. Results show that the proposed model using a constant value of the critical hysteresis angle (Milne’s condition) has good agreement with the experimental results.
[1] A. Esposito, P. Polverino, C. Pianese, Y. Guezennec, A lumped model of single droplet deformation, oscillation and detachment on the gdl surface of a pem fuel cell, ASME 2010 8th International Fuel Cell Science, Engineering and Technology Conference.
[2] F. Celestini, R. Kofman, Vibration of submillimeter-size supported droplets, Physical Review 73 (1).
[3] A. Milne, A. Amirfazli, Drop shedding by shear flow or hydrophilic to superhydrophobic surfaces, Langmuir 25 (24) (2009) 14155–14164.
[4] F. Y. Zhang, X. G. Yang, C. Y. Wang, Liquid water removal from a polymer electrolyte fuel cell, Journal of The Electrochemical Society 153 (2) (2006) A225–A232.