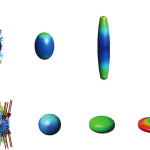Delve into a diverse collection of research papers produced by the esteemed Droplet Dynamics Group, conveniently accessible on Scholar. Some of the most pertinent articles include:
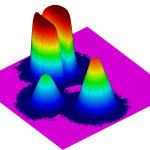
- Machine Learning-Driven Prediction of Accompanying Droplet Structures Based on Primary Droplet ShapeWe are excited to share that our latest research, “Machine Learning-Driven Prediction of Accompanying Droplet Structures Based on Primary Droplet Shape,” has just been published in Physics of Fluids . In this paper, we implement neural networks to infer the presence or absence of secondary droplet structures from the morphology of primary droplets, offering real-time
- DDG published a paper on EHD in the highly impacting Archives journalDroplets team has published a review paper titled Computational ElectroHydroDynamics in microsystems: A review of Challenges and Applications in Archives of Computational Methods in Engineering, (accepted 10/05/2024). This paper is the first attempt at rigorously presenting electrohydrodynamics from the modeling perspective. Governing equations and the issues related to their numerical representation are presented together with
- New redistancing technique for two-phase problems acceptedA. Hashemi, M.R. Hashemi, P. Ryzhakov, R. Rossi. Optimization-based Level-Set Re-initialization: A Robust Interface Preserving Approach in Multiphase Problems. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2023. IF(2022) 7.6, Q1 (JCR). Accepted 13/12/2023. In spite of its overall efficiency and robustness for capturing the interface in multiphase fluid dynamics simulations, the well-known shortcoming of the
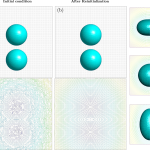
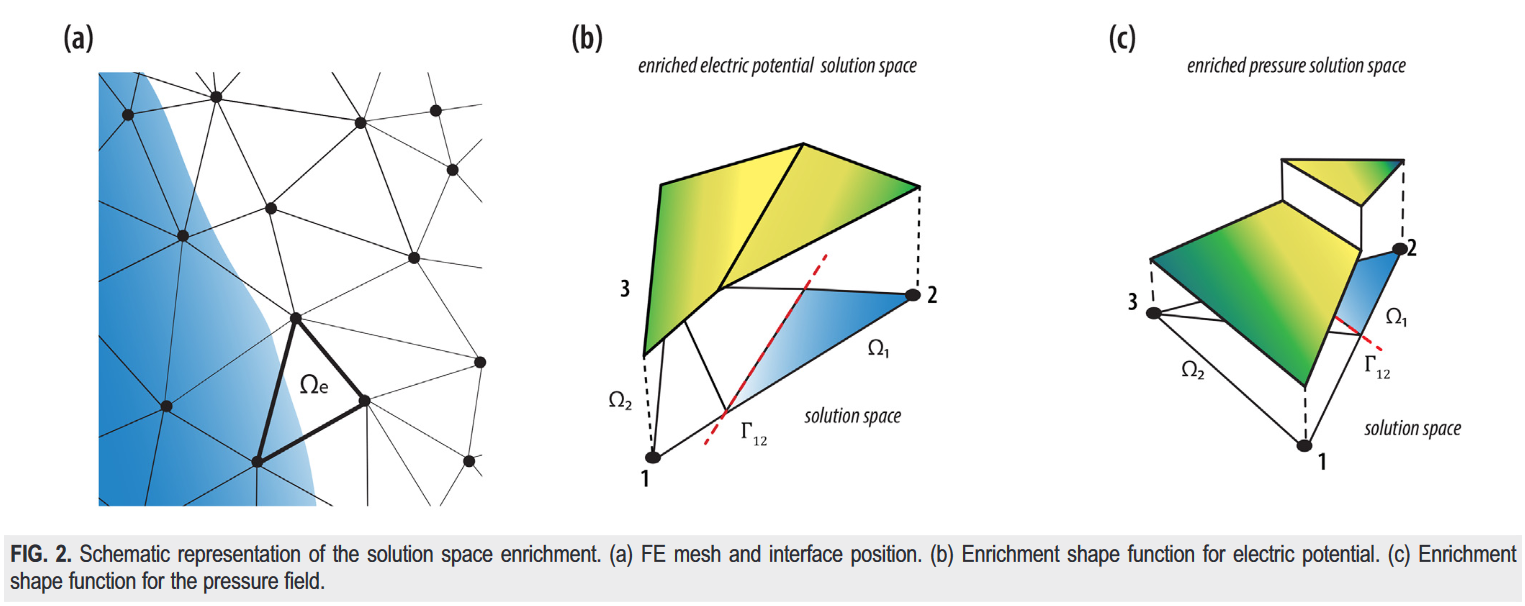
- Enriched FEM for EHD problemsAn enriched finite element/level-set model for two-phase electrohydrodynamic simulations In this work, a numerical model for the simulation of two-phase electrohydrodynamic (EHD) problems is proposed. It is characterized by a physically consistent treatment of surface tension as well as a jump in the electric material properties. The enriched finite element (FEM formulation is capable of
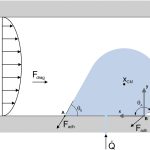
- Droplet spreading using PFEMA particle finite element based model for droplet spreading analysis In this paper, a particle finite element method (PFEM) based model is proposed to analyze the dynamics of droplet spreading on solid substrates (wetting). In order to predict the spreading rate of the droplet on the solid substrate and track the corresponding contact angle evolution,
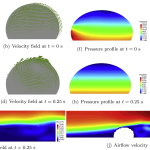
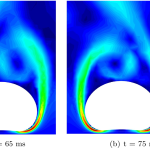
- Droplet dynamics in PEFCNumerical study of droplet dynamics in a polymer electrolyte fuel cell gas channel using an embedded Eulerian-Lagrangian approach In this paper, an embedded Eulerian-Lagrangian formulation for the simulation of droplet dynamics within a polymer electrolyte fuel cell (PEFC) channel is presented. Air is modeled using an Eulerian formulation, whereas water is described with a Lagrangian
- Droplet dynamics modeling in fuel cells via PFEMOn the application of the PFEM to droplet dynamics modeling in fuel cells In this paper, the Particle Finite Element Method (PFEM) is used to develop a model to study two-phase flow in fuel cell gas channels. First, the PFEM is used to develop the model of free and sessile droplets. The droplet model is
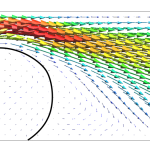
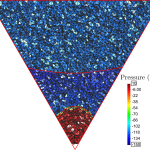
- Droplet dynamics on the GDL surface of a PEM fuel cellA semi-analytical model for droplet dynamics on the GDL surface of a PEM fuel cell cathode In this work, a semi-analytical model of a water droplet emerging from a gas diffusion layer pore in a PEFC channel is developed. From the analysis of the drag coefficient it can be concluded that using a spherical drop
- Droplet dynamics and contact-angle hysteresisTowards Droplet Dynamics Simulation in Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells: Three-Dimensional Numerical Modeling of Confined Water Droplets with Dynamic Contact Angle and Hysteresis This work focuses on three-dimensional simulation of the dynamics of droplets with contact–angle hysteresis (CAH). Generally, hysteresis is associated with the pinning of the contact [1] and characterized by receding and advancing
- Solving advective transport problems using BFECCAn Enhanced Non-Oscillatory BFECC Algorithm for Finite Element Solution of Advective Transport Problems In this paper, the “back and forth error compensation correction (BFECC)” methodology is utilized to improve the solvers developed for the advection equation. The necessary requirement for obtaining a non-oscillatory solution is that the solver embodies discrete maximum principle DMP [1]. Therefore,
- Immiscible multi-fluidsAn embedded approach for immiscible multi-fluid problems In this work, an embedded formulation for the simulation of immiscible multi-fluid problems is proposed. The proposed method is particularly designed for handling gas-liquid systems. Gas and liquid are modeled using the Eulerian and the Lagrangian formulation, respectively. The Lagrangian domain (liquid) moves on top of the fixed
- Two-phase incompressible fluid flows with surface tensionAn Enriched Finite Element/Level-Set Method For Simulating Two-Phase Incompressible Fluid Flows With Surface Tension In this work, a finite element method (FEM) is introduced to simulate surface tension dominated flow of two immiscible fluids. The method proposes an enriched space, created by standard FEM shape functions for capturing both strong and weak pressure discontinuities. Discontinuities
- A surface tension model for droplet dynamicsAn implicit surface tension model for the analysis of droplet dynamics The present work introduces a model which includes an implicit surface tension term in an adopted Lagrangian incompressible framework. The model is applicable to any model where the interface is represented by a moving boundary mesh. The Lagrangian framework is adopted to model the
- Droplets exposed to electric field (EHD)An enriched finite element/level-set model for two-phase electrohydrodynamic simulations In this work, a numerical model for the simulation of two-phase electrohydrodynamic (EHD) problems is proposed. It is characterized by a physically consistent treatment of surface tension as well as the jump in the electric material properties. The formulation is based on finite element method enriched
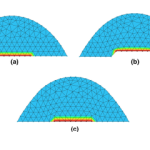
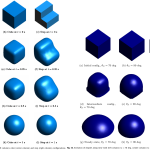
- Droplet spreadingThree dimensional modeling of liquid droplet spreading on solid surface: An enriched finite element/level-set approach A physically consistent approach is introduced to simulate dynamics of droplets in contact with solid substrates. The numerical method is developed by introducing the molecular–kinetic model within the framework of the level-set/enriched finite element method and including the theoretically resolved